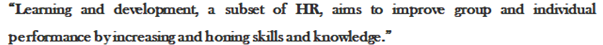Figure 1- Learning and Development (Kirkwood, 2017)
In today Human resource is considered as the main resource that decide successive of any company. According to Kirkwood (2017) research done among USA multinational companies, identified that company successive is depended on ability of updating employees with business environment changes. It can be evaluated that, in order to maintain competitive advantage constantly, it is a main job of HRM to develop employees’skills and knowledge in according to changes in business environment via Learning and development (L&D) and ensure stability.
Figure 2 - Definition of Learning and Development (HRZONE, 2010)
Chandrasekhare (2011) stated there are two main L&d types.Table 1- Learning and Development methods
In 21st century digital age, most of the companies practice L&D by technology based learning. Such as PC based programmes, multimedia, interactive videos, web based training and etc, that ensure more trainer’s involvement on trainees comparing to other learning methods, which will enhance employee knowledge and skills.
According to Cindy (2007) research done among London Gas well drilling company’s employees highlighted that, employees who participate for company training have no turnover intention or neglectful behaviors. It can be argued that, L&D not only improve employees’ knowledge and skills, it stops turnover intention and unethical behaviors, which will ensure companies to maintain a good organizational culture.
But in order to implement L&d programmes, HR will have to invest money with a risk as Berger, Fulford, and Krazmien (2008) research done among US top companies’ lower-level employees identified, though most of companies spend more than $40 billion per year on L&D, employees doesn’t knowing the value of it. It indicates that, though HR invest money on L&D, as employees do not get maximum benefit on improving their knowledge and skills and contribute them for company successive, HR will be pulled for being a cost center though the goal is to become a profit center. HR will have to demonstrate the value of L&D for each and every level of employee to get maximum benefit of it, in where it has become a challenge for HR to keep L&D as a top priority in an organization and convey value of it specially for lower level employees.
With globalization, today most of multinational companies are operated in different geographical areas. But as L&D have to be consistent, it is a challenge for HR for providing consistent training due to geographic limitations, increased costs, language barriers, translation issues, and virtual training needs.
References
Berger. F, Fulford. M., and Krazmien. M. (2008). Human Resources Management in the 21st Century: Predicting partnerships for prifits. Ithaca: Cornell University.
Chandrasekhare. B. (2011). Management. Support to "Child Education and Eradicate Child Labour System" , pp-4-8.
Cindy. W. (2007). 21st-Century Human Resource Management Strategic Planning and Legal Issues. London: Press.
HRZONE. (2010). Learning and Development? Available on: HRZONE: https://www.hrzone.com/hr-glossary/what-is-learning-and-development. Accessesd on 5th July 2018 at 8.36pm.
Kirkwood, C. (2017). What Are Some Challenges of HR With Training & Development? Career Trend , pp-4-9.
|
Thameera's HRM Coner
MN7181 MODULE GUIDE People and Organizations: Principles and Practice in a Global Contexts
Thursday, July 5, 2018
Learning and Development and HRM
Generational Shift and Human Resource Management
Wednesday, July 4, 2018
Work Life Balance and HRM
Figure 1- Work Life Balance (Yatin, 2017)
Work and home can be figured as the most important sectors
in any person’s life. For employees managing the balance between work and life
will decide behaviors and attitudes of that person towards company.
What is Work-life Balance (WLB)?
Figure 2 - Definitions of WLB (Shodhganga, 2017)
By considering all definitions, according to author’s
perspective WLB is proper prioritizing between “work” and “life”. Sanichar (2004) stated, there are many factors
influencing WLB.
Figure 3- WLB
effecting factors (Sanichar, 2004)
According to research done by Kurtzleben (2013) among US
people, both male and female are increasing their stress level due to lack of
WLB that cannot be even controlled by HRM. It can be evaluated that, employee WLB
effecting factors can be controlled by HRM only up to a limited extend, which
enables a great challenge. Most of the time HR will directly able to control
organizational factors, but only limited influence can be done on individual, societal
and other factors.
According to CIPD Research
Report (2009), a research done among London multinational companies’ employees,
it has been identified a positive relationship between WLB and employee
commitment. It can be analyzed that employees who have great WLB will have
good performance and commitment for company, which has been a key contemporary issue for HR for ensuring WLB on each and every employee.
According to Clutterbuck (2003), study done on Roffey Park
Institute, 38% of the sample of employees considers leaving current employer to
gain better WLB, even if it meant reduced pay and low percentage of employees make
use of available WLB practices. It can be analyzed that, employees worth WLB
more than money and possibility of maintaining employee WLB by HR influence on
company talent retention. As HR goal is to become a profit center, though it
creates cost, HR invest money with a risk on WLB programmes, assuming for
getting better performances and talent retention from employees. But in most of
companies, implementing WLB programmes is not enough to ensure employee WLB,
proper trainings and knowledge must also be provided about WLB programmes in order
to convert this HR invest in to a profit center, which has been a great contemporary
issue in today business world.
References
CIPD Research Report. (2009). Employment Trends
Survey: People Driving. Pertemps and Confederation of British Industry
, pp-3-9.
Clutterbuck. D. (2003).
Managing Work-life Balance: A guide for HR in achieving organizational and
individual change. London: UK Chartered Institute of Personnel and
Development.
Kurtzleben. D. (2013). Men
and Women Both Stressed About Work-Life Balance. Staff Writer , pp-10-15.
Sanichar, A. (2004).
The strategic implications and management considerations of work/life
programmes. . Journal of Contemporary Management. , pp-31-44.
Shodhganga. M. (2017).
Work Life Balance and Job Satisfaction . Bitstream , pp-7-9.
Yatin. (2017). How to
strike a healthy work life balance – 5 key elements. Work Culture , pp-
2-9.
Employee Engagement and HRM
 |
| Figure 1 - Employee engagement (Amling, 2017) |
Organizations have realized that in today’s constantly
changing business scenario, the most valuable recourse which needs to be
leveraged is Human. This means not just attracting and retaining employees, but
also keeps motivated and committed for organizational goals achieving which is
employee engagement.Many authors have
defined employee engagement as below.
Tuesday, July 3, 2018
Migration and Human Resource Management
Sunday, June 17, 2018
Workforce diversity and HRM in 21st Century
According to Loysk (1996), with
globalization, as the whole world became a village, today people are no longer living
and working in an insular environment. They are part of a worldwide economy
competing within a global framework. According to Burns & Barton (2012) a
research done in U.S workforce, companies are required to be interact among people
from diverse backgrounds in order to maintain competitiveness in the global market.
According to Moorhead & Griffin (1989),
workforce diversity can be defined as,
Figure 2 - Definition of Workforce diversity (Moorhead & Griffin, 1989)
According to SHRM (2007), research
done among 5000 SHRM HR proffesionals, in order to manage diversity, HRM
practisesis must adapt to accommodate a multicultural work environment. Loysk (1996)
stated that, bringing all the people of different nature under a one roof of
organization the key responsibility of HRM on diversity management.
According to Bedi & Lakra
(2014), in past diversity was treated as a legal issue which is only a challenge
but now in 21st century accoring to Roosevelt (2001), companies
realize that diversity is a reality to build a stronger, competitive enterprise
rather than something deal with.
Challenges of workforce
diversity on HRM in 21st Century
According
to Morais, Pena, Shacket, Sintilus, & Ruiz (2014),
research done on Starbucks, as an international company, HR is
responsible on recruiting qualified candidates while promoting diversity by recruiting employees from all genders,
races, religions, nationalities and etc. where two roles appear to be at cross purposes to each other,
which is a great challenge for HRM in today.
According
to Patrick & Kumar (2012), a research done
on IT sector of India, training employees to be sensitive and accept to
cross-cultural differences and offering foreign language trainings to increase
inclusiveness, is a challenge for HRM as it pushes HRM more for a cost center
inside the company.
Especially
in Multinational companies practicing mindful of
‘Think Global, Act Local’ approach in order to motivate highly
qualified culturally diverse professional and assure
foreign professionals are not a threat for
career advancement of local professionals is a great challenge
of HRM. At last according to SHRM (2007), author
would suggest for HRM to practice culturally relative perspective (Let's
take the best variety of ways) rather than ethnocentric view (our way is
the best) in the business context to manage diversity in an effective manner.
References
Bedi. P. and Lakra. P. (2014). Workforce Diversity
Management. IOSR Journal of Business and Management (IOSR-JBM) ,
102-107.
Burns. C. and Barton. K. (2012). The State of Diversity in Today’s Workforce. Center for
American Progress, 4-10.
Loysk. B. (1996). Managing
a changing workforce: Achieving outstanding service with today’s employees.
Davie: Workplace Trends Publishing.
Moorhead. G. and Griffin. R. (1989). Organizational Behavior. Indiana: Houghton Mifflin
Company.
Morais. U., Pena. J.,
Shacket. K., Sintilus. L. and Ruiz. R. (2014). Managing Diverse Employees
at Starbucks: Focusing on Ethics and Inclusion. International Journal of
Learning & Development , 35-40.
Patrick. H. A. and Kumar.V. R. (2012). Managing Workplace Diversity: Issues and Challenges. SAGE
Open , 1-15.
Roosevelt, T. (2001). Elements
of a successful “diversity” process. The
American Institute for Managing Diversity: Accessed by: https://www.coursehero.com/file/p5u15p6/Roosevelt-T-R-Jr-2001-Elements-of-a-Successful-diversity-process-The-American/ Accessed on 28th May 2018, 10.29pm.
SHRM. (2007). State of Workplace Diversity Management. Society for Human Resource
Management , 14-19.
Sunday, May 20, 2018
HRM in the Digital Age
The world has changed in cultural, societal and economical
sectors due to digital technological changes. Those changes play a role in employees’
lives and HRM. According to Ashbaugh
and Miranda (2002), in this digital age, HRM has transferred as E- HRM,
as companies have to be adopted for the digital technological changes in
recruit to retire functions, to be success. Evolution of HRM in according to
technology changes is given below.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Learning and Development and HRM
Figure 1- Learning and Development (Kirkwood, 2017) In today Human resource is considered as the main resource that decide succe...

-
Figure 1- Learning and Development (Kirkwood, 2017) In today Human resource is considered as the main resource that decide succe...
-
Figure 1 - Work Life Balance (Yatin, 2017) Work and home can be figured as the most important sectors in any person’s life. For e...
-
Figure 1 - Employee engagement (Amling, 2017) Organizations have realized that in today’s constantly changing business scenario, the...